Methods of testing and diagnosing seborrheic dermatitis (seborrheic), seborrheic dermatitis,
Seborrheic dermatitis, also known as seborrheic dermatitis, is a skin disease that is difficult to treat, and is usually persistent and recurring.
Contents
1. What is oily dermatitis?
Seborrheic dermatitis , also known as seborrheic dermatitis, is a chronic skin disease. Disease caused by a small yeast called Malassezia overgrowth and several other resonant factors located on the skin are considered the cause of the disease.
Seborrheic dermatitis, though not contagious, is a benign skin disease and has almost no serious health effects, but has a lot to do with the aesthetics and psychology of the patient.
When an oily skin inflammation occurs, the skin will flake off into pink patches in areas of the skin or parts that are prone to sebum production such as nose, cheeks, ears, eyebrows, in addition to the scalp, and the skin in front of the chest. or the back skin will also suffer.
Any object can get sick. However, according to research, the age of 18 to 40 years often suffer from seborrheic dermatitis and the rate of men suffering more than women.

2. Causes of oily dermatitis
Currently, the cause of seborrheic dermatitis has not been answered. According to the study, a number of endogenous factors and genes may be considered to be involved in osteoarthritis. At the same time, the presence of fungi is also found in people with oily dermatitis.
Seborrheic dermatitis cannot spread from person to person even in direct contact with an infected person because the disease does not have a contagious agent.
Seborrheic dermatitis is inherited. About 40% of babies are born with osteoarthritis due to a parent with inherited oily dermatitis. Besides, the infected skin is also easily spread from one location to another. Therefore, when sick, patients should proactively treat as soon as they see symptoms of dermatitis for easy, quick treatment and increase the effectiveness of cure and avoid leaving complications.
3. Symptoms of oily dermatitis
The symptoms of osteoarthritis are often different for each person, depending on the location of the seborrheic dermatitis, the condition is severe or mild and can be distinguished in children and adults.
Some typical symptoms can be noticed:
3.1 Expression of oily dermatitis in adults
In adults, the location occurs more commonly on the face, scalp, skin on the upper half of the body. Facial seborrheic dermatitis has butterfly-shaped cheeks, T-zone on the edge of the forehead, between the nose, between the eyebrows, the skin is red, with thin scaly skin.
Seborrheic dermatitis in the scalp causes the scalp to flake in the form of dandruff flakes, resulting in itching and hair loss . People who are sick often have a combination of sebum and dry muscles.
When the weather is hot, sweating that causes itching can increase. Seborrheic dermatitis appears to be worse in winter when the weather is dry. In severe cases, scabs may appear behind the ears, in the ear canal, the arch of the eyebrows, the bridge of the nose, around the nose, chest or shoulders, and areas of skin that have folds.
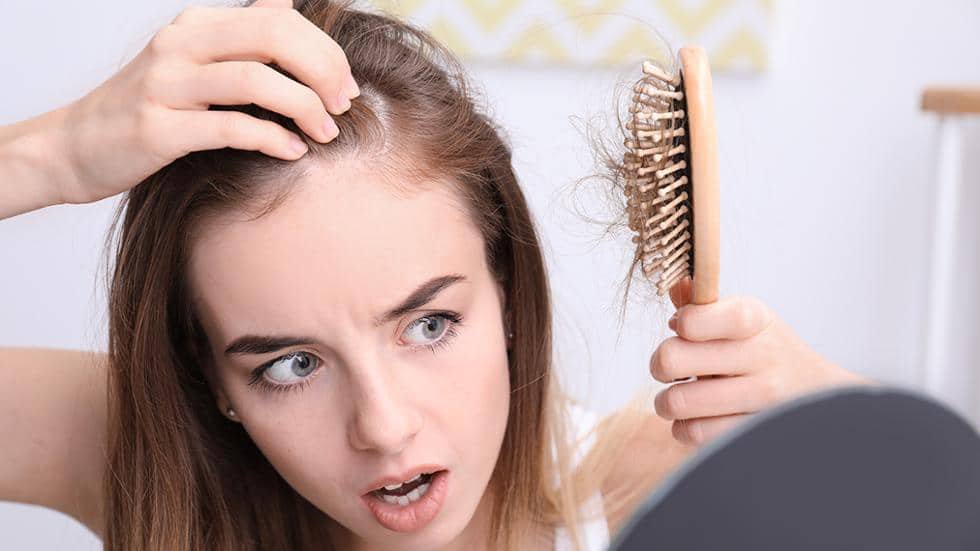

3.2 Symptoms of oily dermatitis in children
Baby's scalp appears greasy, has a thick patch of skin, spreads to the neighboring scalp areas and is difficult to peel. When the disease gets worse, oily dermatitis will spread to the whole body, showing signs of scaly secretion. Scales yellow, skin moist, oily and sticky. Babies get itchy that leads to irritability and fussiness.
4. Treatments for oily dermatitis
Depending on the severity or severity of oily skin inflammation , your doctor will have different treatment options.
4.1 Medication Use
Using medications that help with desquamation, anti-inflammatory and anti-toxic can be prescribed for treatment. In addition, if the cause is found to be the fungus, the doctor may prescribe additional herbal shampoos or soaps that contain special antifungal agents for the patient to use.
In severe cases, a combination of oral and topical drugs. Topical creams containing selenium sulfide, ketoconazole, or corticosteroids ; Combining with immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory creams can be effective.
4.2 Appropriate mode of living
Change habits, daily activities. Seborrheic dermatitis is a disease that is easy to come back, even though it is cured. Prevention is a good way to limit the likelihood of recurrence of the disease as well as help quickly cure it. Some of the following living habits to pay attention to:
- Use oral medications and creams according to the dosage and instructions given by your doctor.
- Avoid direct sunlight, dirt in contact with skin.
- If you experience abnormalities in the body during treatment, you should immediately contact your dermatologist for consultation.
- Do not use your nails to scratch the scalp when washing your hair, but only gently rub your head because using nails can cause abrasions.
- Use mild bath lotions and shampoos that are mildly mild in mild detergent.
- For oily people , be careful when choosing to use cosmetics, do not use cosmetics containing many toxic chemicals and of unknown origin and origin.
- Eat plenty of fiber such as green vegetables, legumes, and fresh fruits.
- Limit the use of alcoholic and stimulant substances such as tobacco, alcohol, and foods high in sugar and grease.
- Exercise regularly to increase resistance, fitness, increase blood circulation, help organs work stably and limit the sebaceous gland increase process.
Source: eupharmas